Bloomington, Ind. — Following the publication of an animal study examining the performance of embolisation coils in arteries1 in the Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology (JVIR) in 2019, a second, similar study,2 published in the May 2023 issue of JVIR, examined fibred and non-fibred embolisation coil performance, this time in the venous system.
In this newly published venous ovine study, fibred Nester® coils and non-fibred coils were deployed in 24 veins in 6 sheep. The study’s data confirmed that fibred coils demonstrate several advantages over non-fibred coils. These advantages include the following:
- Fibres significantly boosted the immediate occlusive capacity of coils. In the study, fibred coils achieved stasis in 5.3 minutes, while non-fibred coils took 9.0 minutes.2
- A significantly lower average radiation dose was required when fibred coils were used: 25.3 mGy for fibred coils compared with 34.9 mGy for non-fibred coils.2
The venous fibre study also substantiated the findings of the earlier arterial fibre study: The two studies found that fewer fibred coils are needed to achieve acute occlusion compared to bare metal coils.1, 2 Both studies confirmed that significantly less coil length is needed if the coil is fibred.1, 2
- In the venous fibre study, on average 5 fibred coils, or 70 cm of fibred coil length, were needed to achieve occlusion compared with 8.75 non-fibred coils, or 122.5 cm of bare metal coil length.2
- In the arterial fibre study, on average 1.3 fibred coils, or 9.1 cm of coil length, were required to achieve occlusion, compared to 2 non-fibred coils, or 22.4 cm of non-fibred coil length, that was needed to obtain occlusion.1
Should the study results translate to the human experience, patients treated with fibred coils could potentially experience shorter procedure times, require fewer implants and have less radiation exposure to achieve the same outcomes.*
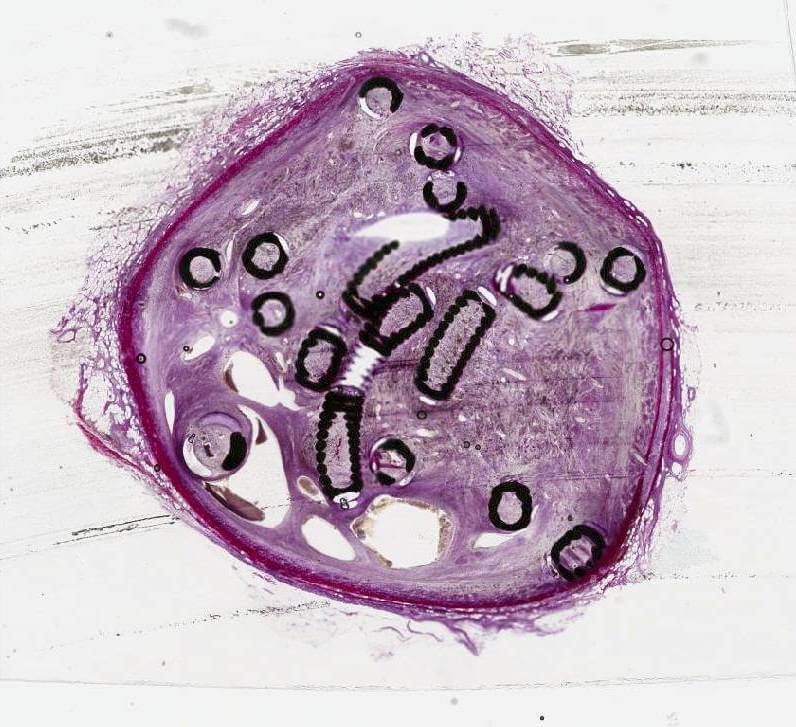
This study used a unique method of generating histologic images of metallic implants by cutting 5µm thin sections of tissue embedded in resin.
In this venous fibre study, a new approach was also applied to generating histologic images. A unique method of cutting 5 µm thin sections of tissue with metallic implants was developed by Cook Research Incorporated (CRI) and Alizée Pathology. Thin sectioning results in clearer and more detailed histologic images, allowing a pathologist to read and interpret tissue changes. An image showing a 5 µm thick microscope slide of Cook embolisation coils in an ovine vein can be seen on the front cover of the May 2023 issue of JVIR and online at www.jvir.org.
“When we see in vivo results like this in studies, we hope the same benefits will be applicable to human patients,” said Remco van der Meel, director of product management for Cook’s Interventional specialty. “We are constantly evaluating our Embolisation portfolio, exploring cutting-edge technology and gathering data to create new technology. Additionally we want to understand how we could best support our customers in achieving the best possible outcomes for patients. This study helps us make data-based decisions on how to best meet the needs for effective embolisation in a cost-efficient manner, while reducing exposure to ionizing radiation for both doctor and patient. These are key elements in today’s healthcare environment.”
To read the full venous animal fibre study, view the article on JVIR’s website. To read the full arterial fibre study article, go here. To learn more about fibred coils, visit our Cook Medical embolisation web page here.
*Definitive conclusions regarding the safety or effectiveness of fibred coils in humans cannot be directly drawn from the results of these animal studies.
About Cook Medical
Since 1963, Cook Medical has worked closely with physicians to develop technologies that eliminate the need for open surgery. Today we invent, manufacture, and deliver a unique portfolio of medical devices to the healthcare systems of the world. Serving patients is a privilege and we demand the highest standards of quality ethics, and service. We have remained family owned so that we have the freedom to focus on what we care about: our patients, our employees, and our communities.
Find out more at CookMedical.eu, and for the latest news, follow us on Twitter, Facebook and LinkedIn.
1 Trerotola SO, Pressler GA, Premanandan C. Nylon fibered versus non-fibered embolization coils: comparison in a swine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30(6):949–955.
2 White SB, Wissing ER, Van Alstine WG, et al. Comparison of fibered versus nonfibered coils for venous embolization in an ovine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2023;34(5):888–895.
