Haemostasis: The cessation of bleeding via mechanical or chemical means. Haemostasis is most commonly achieved by two mechanisms, tamponade and coagulation.
Examples of the tamponade mechanism of haemostasis include tourniquets, clipping, and cyanoacrylate sealants.
Examples of the coagulation mechanism include thrombin, argon plasma, RF electrocautery.
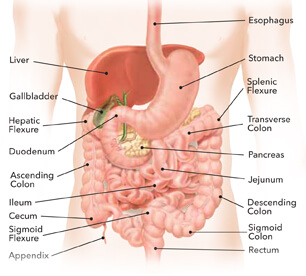 Where does Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding occur?
Where does Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding occur?
70 to 75% in the upper GI tract – UGIB
(proximal to ligament of Treitz) Oesophagus, stomach, duodenum, biliary/pancreatic systems
25 to 30% in the lower GI tract – LGIB
(distal to ligament of Treitz) Jejunum and ileum, colon, anus
Diagnostic Procedure
Endoscopy is effective in diagnosing and treating most causes of GI bleeding. Studies show endoscopic therapy significantly reduced rebleeding, the need for emergency surgery and mortality.
- Upper GI: oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
- Lower GI: colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of bleeding – variceal or nonvariceal bleeding
Variceal bleeding –
The underlying pathophysiology is due to elevated portal pressure transmitted to oesophageal and gastric varices.
Nonvariceal bleeding –
The underlying mechanisms involved are either arterial haemorrhage, such as in ulcer disease and mucosal deep tears, or low pressure venous hemorrhage, as in angiodysplasia and other ectasias.
Several meta-analyses including more than 1,000 patients have shown that thermal haemostatic devices, injection therapy, and clips either in combination or alone are all highly successful in achieving initial haemostasis in bleeding peptic ulcer disease.
Clips and thermal therapy, either alone or paired with injection therapy, are superior to injection therapy alone in preventing rebleeding and the need for surgery. There is no significant difference between clips and thermal therapy in rebleeding rates, the need for surgery, and mortality.
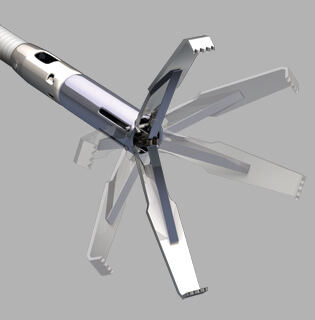
Endoscopic Treatment Modalities
Mechanical
 |
 |
Thermal
Injection